close
Choose Your Site
Global
Social Media
Views: 0 Author: Site Editor Publish Time: 2025-11-17 Origin: Site









As 2026 approaches, takeout packaging is evolving rapidly. With more consumers demanding eco-friendly solutions, businesses must adapt to stay competitive. Sustainability is no longer just a trend—it’s a necessity.
In this article, we’ll explore the top 10 takeout packaging trends for 2026. You’ll discover how businesses can align with sustainability, meet consumer expectations, and comply with evolving regulations.
The growing demand for eco-friendly takeout packaging is undeniable. Over 82% of consumers are willing to pay a premium for packaging that is sustainable, showing that the demand for environmentally responsible solutions is stronger than ever. This shift in consumer behavior is driving foodservice businesses to reconsider their packaging materials. Eco-conscious consumers are not just looking for convenience—they are actively seeking brands that align with their values.
Adopting sustainable packaging is no longer a choice for companies looking to stay competitive in the market; it's a necessity. Whether it's compostable materials or reusable containers, offering an environmentally friendly option is becoming essential for businesses to attract and retain customers.
Governments around the world are tightening regulations related to packaging waste. From the European Union’s ban on certain plastic items to stricter laws in North America, businesses face mounting pressure to adopt recyclable or compostable packaging. Many regions are implementing extended producer responsibility (EPR) laws, holding businesses accountable for the recycling of their packaging waste. For companies, this means that adapting to new packaging requirements is not just about customer satisfaction but also about staying compliant with regulatory frameworks.
By 2026, businesses that embrace these regulations will be well-positioned to thrive, ensuring they avoid penalties and capitalize on the growing market for eco-friendly packaging.
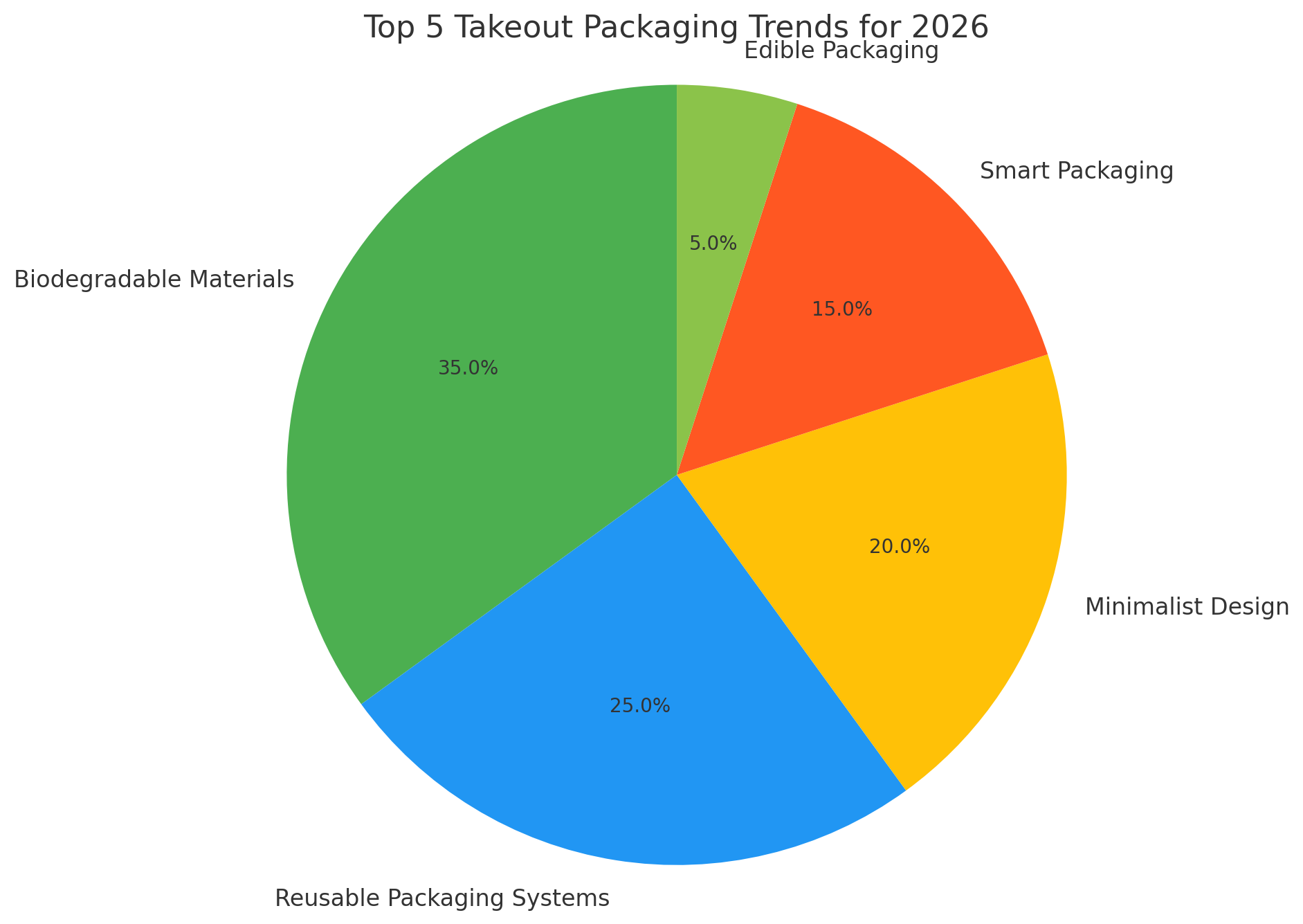
Trend | Description | Benefits |
Biodegradable Materials | Compostable paper, PLA, bioplastics like PHA | Reduces waste, eco-friendly, meets regulations |
Reusable Packaging Systems | Containers that can be returned, cleaned, and reused | Reduces single-use waste, strengthens customer loyalty |
Minimalist Design | ‘Right-sized’ packaging to fit the food without excess materials | Reduces material use and shipping costs |
Smart Packaging (QR Codes) | Packaging with QR codes for customer engagement and transparency | Enhances customer interaction and trust |
Edible Packaging | Packaging made from edible materials like seaweed or rice | Eliminates packaging waste, innovative solutions |
Circular packaging is a concept that is gaining traction, particularly in the takeout food sector. Closed-loop systems that allow packaging to be reused or refilled are becoming more common. This trend involves designing packaging that can be returned, cleaned, and used again, reducing waste and extending the lifecycle of materials. For example, some restaurants are experimenting with reusable containers for takeout orders, where customers can return them for a discount or rewards points.
As consumers become more aware of waste issues, businesses that implement circular packaging models will not only benefit from cost savings but will also build stronger relationships with environmentally conscious customers.
Compostable paper and cardboard are becoming key materials in takeout packaging. These materials, made from renewable resources, break down naturally in composting environments, offering a viable alternative to traditional plastics. For foodservice businesses, choosing compostable paper and cardboard containers is a simple yet effective way to reduce their environmental footprint.
Not only are these materials biodegradable, but they also ensure that food stays secure and safe during transport. Restaurants looking to meet both sustainability goals and customer expectations are increasingly turning to these options, especially as composting programs become more accessible in urban areas.
Bioplastics such as PLA (polylactic acid) and PHA (polyhydroxyalkanoates) are gaining popularity due to their renewable nature. PLA is made from plant-based materials like cornstarch, while PHA is produced by microorganisms. Both options are compostable and offer an alternative to traditional plastics that can take hundreds of years to break down.
The adoption of bioplastics, however, comes with challenges. These materials can be more expensive than traditional plastics, and their disposal methods are still being optimized. Nevertheless, their potential for reducing plastic waste makes them a strong candidate for the future of takeout packaging.
Material | Strengths | Best For | Disadvantages |
PLA (Polylactic Acid) | Made from renewable plant-based sources | Cold food items | Limited heat resistance |
Bagasse (Sugarcane) | Heat-resistant, strong, and compostable | Hot food items | Requires industrial composting facilities |
Bamboo | Fast-growing, biodegradable | Takeout containers, utensils | May be more expensive than alternatives |
Palm Leaves | Natural, heat-resistant, sturdy | High-end food packaging | May not be widely available |
Sugarcane bagasse and bamboo are other promising alternatives for takeout packaging. Bagasse, a byproduct of sugar production, is a sturdy, biodegradable material that is particularly useful for hot foods. Bamboo, with its fast-growing nature and sustainability credentials, is increasingly being used for takeout containers and utensils.
These materials are strong, heat-resistant, and completely biodegradable, making them ideal choices for packaging that needs to withstand hot food temperatures. As more businesses prioritize sustainability, these alternatives are set to become mainstream choices for takeout packaging.
Reusable takeout containers are emerging as a game-changer in the foodservice industry. Forward-thinking restaurants and food delivery services are introducing programs where customers can opt for reusable containers instead of disposable ones. These containers are returned for cleaning and reuse, reducing the overall waste generated by single-use packaging.
Real-life examples include Just Salad, which has been offering reusable bowls for years, and Starbucks, which has experimented with reusable coffee cups in certain locations. These businesses are not only helping reduce waste but also creating a loyal customer base that values sustainability.
While reusable packaging systems offer significant environmental benefits, they come with logistical challenges. Businesses must find ways to ensure containers are properly sanitized between uses, track returns, and manage the inventory of reusable packaging. These challenges can be addressed by partnering with third-party logistics providers or by setting up efficient return systems in-store or via delivery services.
Educating consumers on the benefits of reusing packaging and incentivizing their participation with discounts or loyalty points can further streamline the process.
Packaging Type | Environmental Impact | Advantages | Challenges |
Single-Use Plastic | Contributes to landfills and ocean pollution | Low initial cost | High environmental cost and waste |
Reusable Containers (Glass/Plastic) | Reduces waste when returned and reused | Long-term cost savings, customer loyalty | Requires return systems and logistics |
Biodegradable Alternatives | Breaks down naturally in compost | Reduces landfill waste, eco-friendly | May require special disposal methods |
Incentive programs are essential to the success of reusable takeout systems. Offering customers rewards for returning their containers or providing discounts for using reusable packaging can encourage participation and create a sense of ownership. By making it easy and rewarding for consumers to return containers, businesses can significantly reduce waste and improve customer loyalty.
One of the key packaging trends for 2026 is the shift towards ‘right-sized’ packaging. This concept involves using the minimum amount of material necessary to protect and deliver food. By eliminating excess packaging, foodservice businesses can reduce costs, improve operational efficiency, and minimize waste.
‘Right-sized’ packaging also allows businesses to reduce their carbon footprint by cutting down on transportation costs and material usage. This minimalist approach resonates with eco-conscious consumers who appreciate brands that prioritize efficiency and sustainability.
In the same vein, businesses are moving away from multi-layer packaging that can increase waste. Packaging that is simple and effective—without unnecessary layers—reduces the overall environmental impact. For example, eliminating plastic liners or reducing the use of foam inserts can significantly cut down on packaging waste.
Simplicity in packaging design is more than just an aesthetic choice—it’s a reflection of a brand’s commitment to sustainability. Clean, minimalist designs often use fewer materials and are easier to recycle. Consumers are drawn to packaging that aligns with their environmental values, and a straightforward, minimalist design can communicate a brand’s commitment to sustainability without any extra fluff.
Smart packaging that incorporates QR codes is becoming increasingly common. By scanning these codes, customers can access information about the sustainability of the packaging, track their carbon footprint, or even access discounts and promotions. This feature enhances the customer experience by offering more transparency and fostering deeper engagement with the brand.
Smart sensors embedded in packaging can monitor food freshness and safety during delivery. These sensors track temperature, humidity, and other conditions, ensuring that food arrives in optimal condition. This type of smart packaging adds another layer of value by improving the overall customer experience, ensuring that food stays fresh, and reducing waste caused by spoilage.

Imagine packaging that can be eaten rather than thrown away. This concept is becoming a reality with innovations in edible packaging made from materials like seaweed, rice, and plant-based substances. Edible packaging not only eliminates waste but also offers an exciting way to innovate in the foodservice industry.
While this technology is still in its infancy, it presents a potential game-changer for businesses looking to reduce their environmental impact. For now, it’s primarily used in specific applications like water packaging or dessert containers, but its potential could be much broader in the coming years.
While edible packaging may seem like a novel solution, consumer acceptance is still a work in progress. Some customers may hesitate to embrace this new concept due to unfamiliarity or concerns about taste and texture. However, as the environmental benefits become more widely understood and the technology improves, edible packaging could become a mainstream solution for takeout packaging.
Generation Z is driving the demand for more sustainable and transparent packaging. This generation values authenticity and wants to support brands that align with their environmental values. For businesses, this means that adopting sustainable takeout packaging can be a powerful way to connect with younger consumers and build long-term brand loyalty.
Personalized packaging is becoming more popular as businesses seek to create emotional connections with their customers. Whether it’s a special design for a limited-time menu item or custom messaging on packaging, offering consumers a unique experience helps set a brand apart. This trend not only adds value but also reinforces the brand’s commitment to creativity and sustainability.
The use of recycled materials in takeout packaging is becoming more common as businesses look for ways to reduce their environmental impact. Recycled plastics, for example, can be repurposed into packaging materials, helping to keep plastic out of landfills and reduce the need for virgin materials. By embracing recycled plastics, foodservice businesses can contribute to the circular economy while offering affordable packaging solutions.
Lighter packaging materials are another trend that can help reduce a business’s carbon footprint. By using lighter packaging, companies reduce the energy required for transportation, which in turn lowers emissions. Whether it’s lightweight plastics or thinner cardboard, lighter packaging is a simple yet effective way to improve efficiency and sustainability.
As the demand for sustainable takeout packaging grows, businesses must stay ahead of consumer expectations and regulations. Embracing trends such as biodegradable materials, reusable systems, minimalist design, and smart packaging will help reduce environmental impact. Early adaptation offers a competitive advantage. Companies like Lixin Plastic Packing Company provide innovative packaging solutions, ensuring businesses can meet sustainability goals while offering high-quality, eco-friendly products that resonate with customers.
A: The top trends include biodegradable materials, reusable packaging systems, minimalist design, and smart packaging with QR codes. These trends aim to meet consumer demand for sustainability and comply with regulations.
A: Sustainable takeout packaging is crucial due to growing consumer demand for eco-friendly options. It helps businesses reduce waste, meet regulatory requirements, and build stronger customer relationships by offering eco-conscious solutions.
A: Start by implementing a returnable container program. Offer incentives like discounts or loyalty points for customers who return containers, helping to reduce waste while promoting sustainability in takeout packaging.
A: Biodegradable materials, like compostable paper and sugarcane bagasse, break down naturally, reducing environmental impact. They provide a sustainable alternative to traditional plastics and are preferred by eco-conscious customers.
A: Smart packaging with features like QR codes allows businesses to engage customers with sustainability stories, offer discounts, and provide tracking information for food safety. It creates a more interactive and transparent experience.